BFLEX
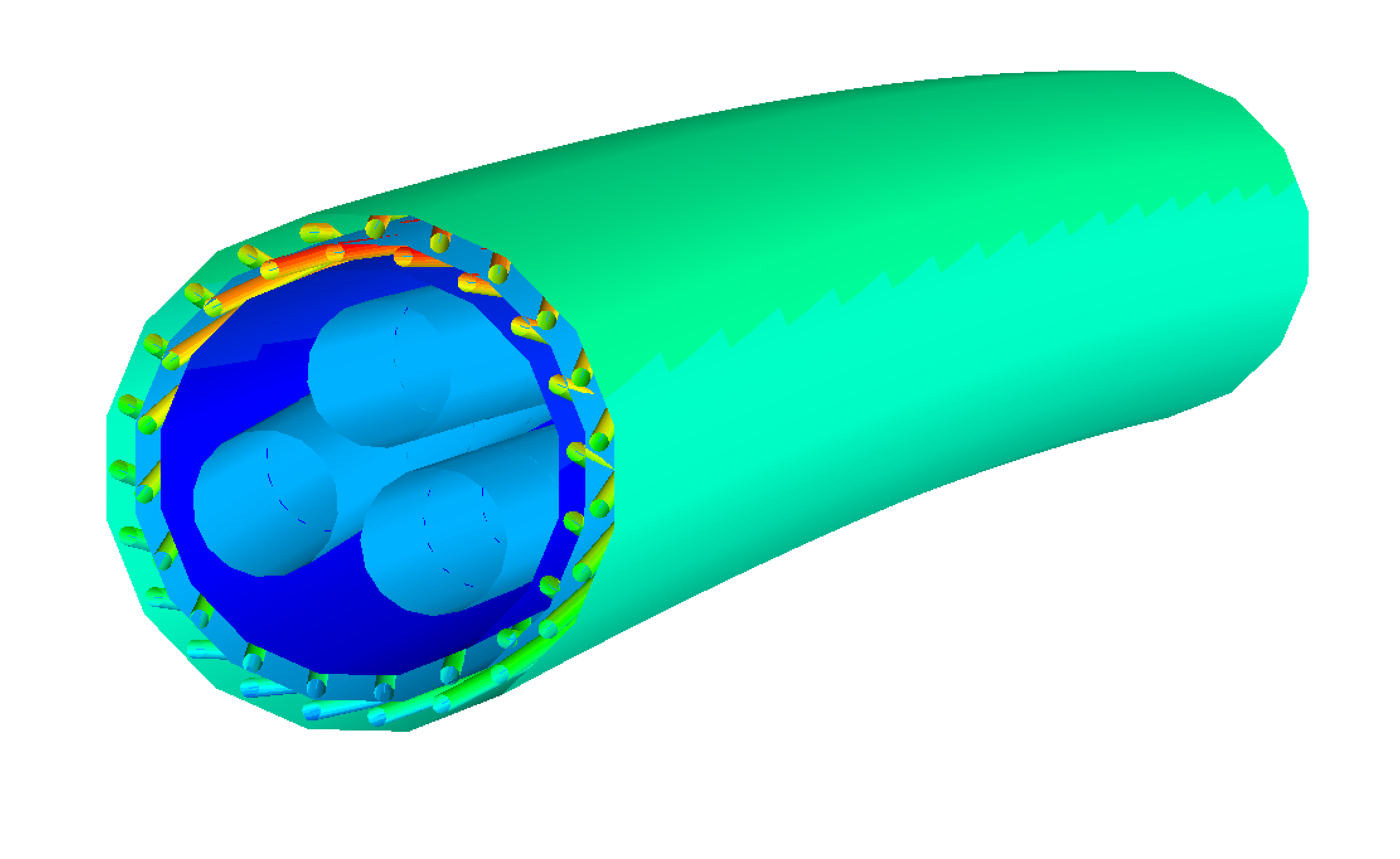
The BFLEX program system is a special-purpose finite element tool developed for analysis of flexible pipes, umbilicals and power cables during load-out, installation and under in-service load conditions.
For non-bonded flexible pipes, BFLEX is widely used for ULS and FLS assessment of tensile and pressure armor wires. The non-linear behavior of the flexible pipes under complicated load conditions can be precisely predicted. The performance has been verified by full scale laboratory measurements with excellent agreement.
Application examples

Lateral buckling of armour wires
Under axial compression in deep waters, the armour wires may buckle laterally. The cyclic buckling process can be modelled in detail using the repeated unit cell approach, or by using a less detailed model of a few pitches.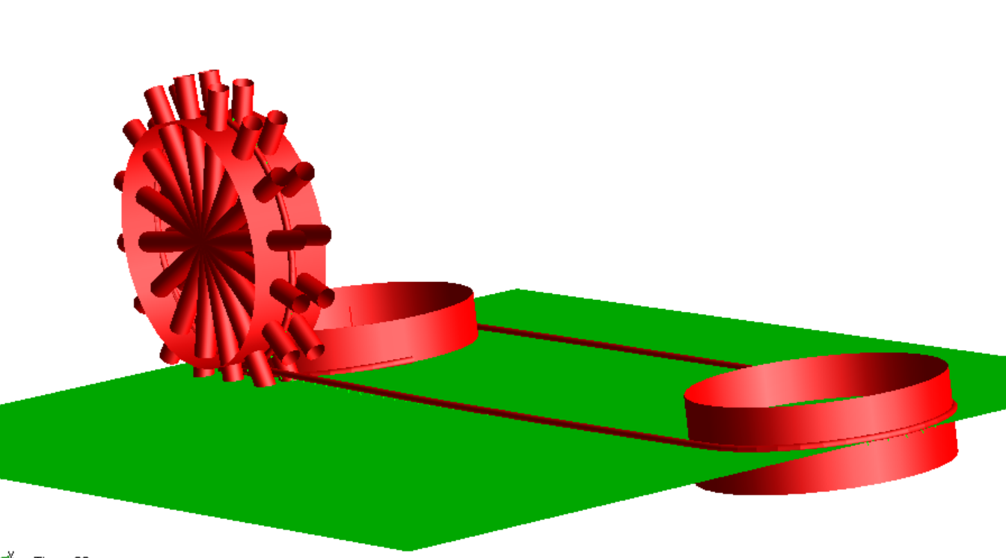
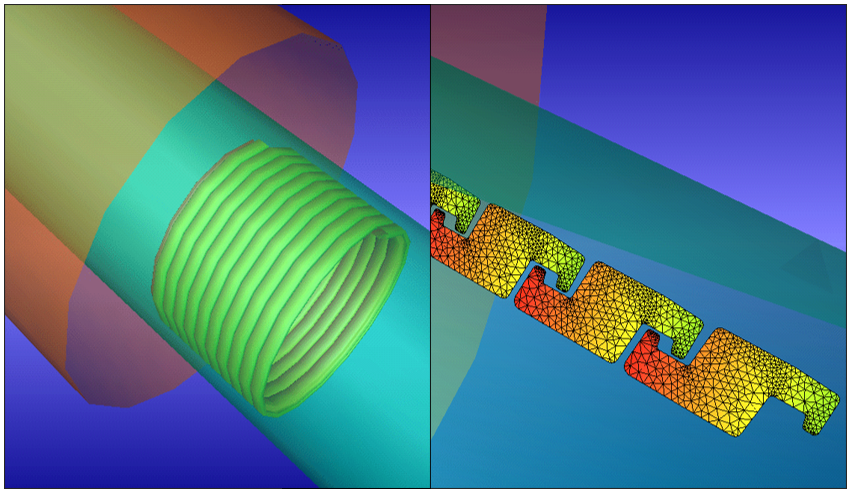
Spooling operations
Spooling of flexible pipes for example during load-out may lead to torqe build-up in the pipe. Contact towards rollers and spools can be modelled. By a layer approach for the helical components the model size can be reduced such that a suficient length can be included.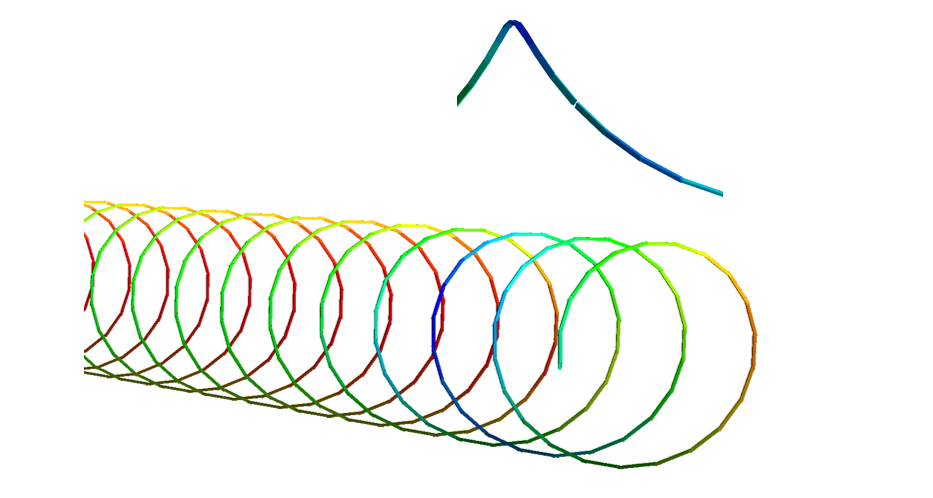
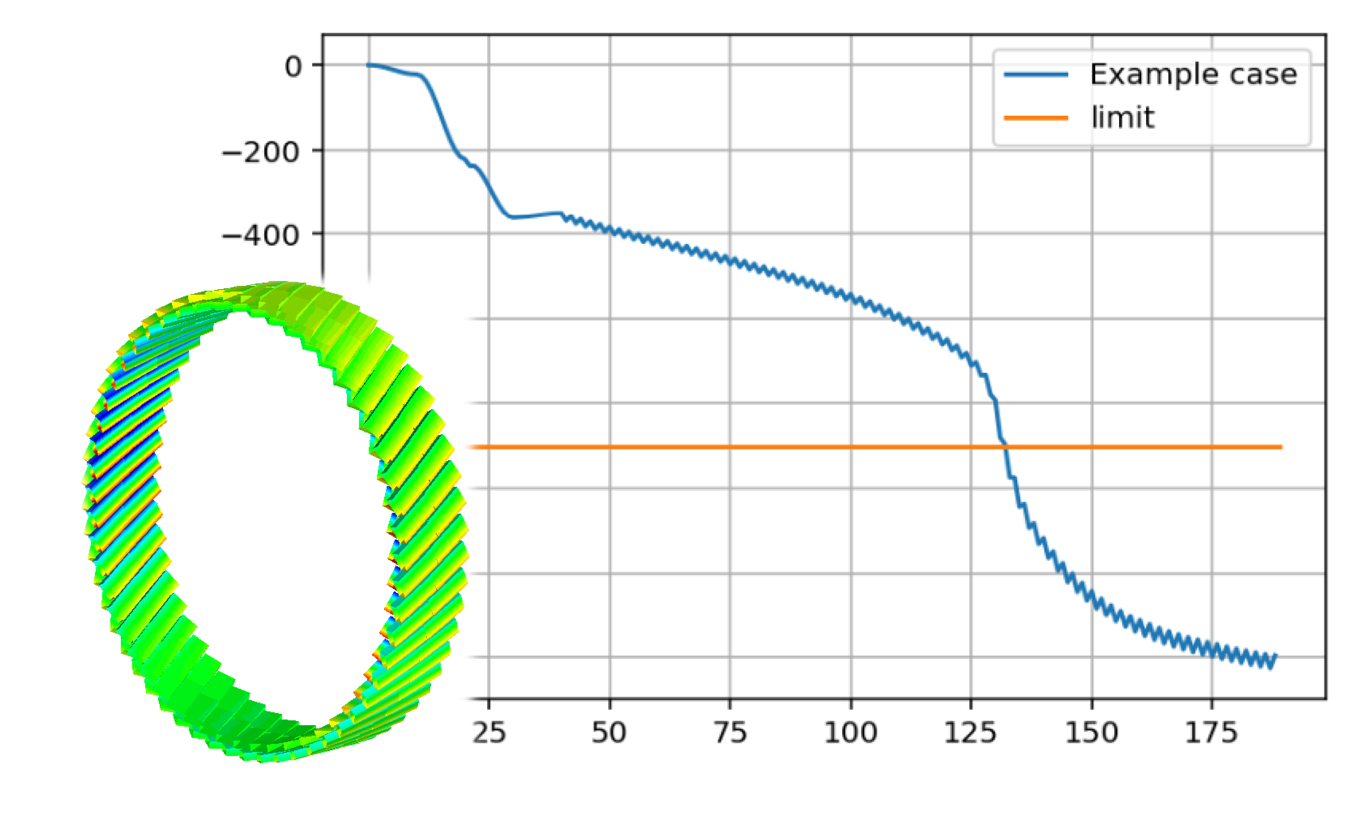
Broken armour wire
The stress release around the point of a single wire break can be modelled by disconnecting nodes in the wire, or by changing the properties of single elements at a selected time during the analysis.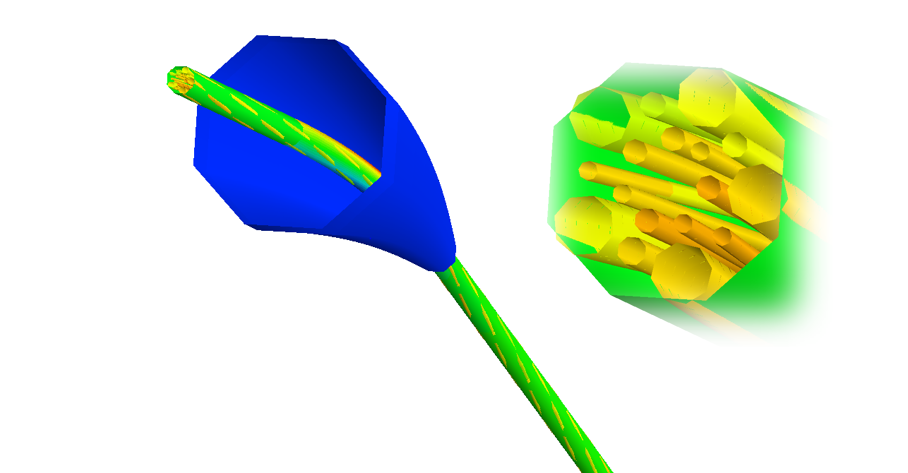
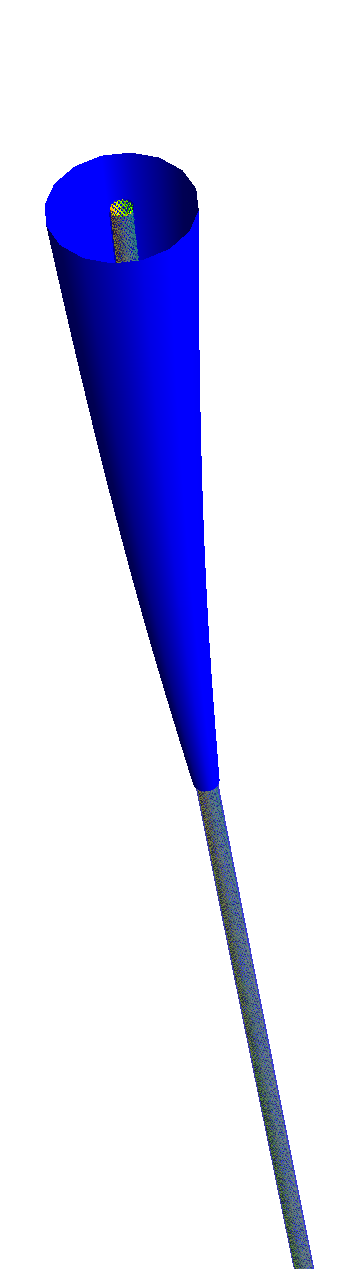
Umbilical hang-off
The 3D effects of a pipe throgh bend stiffener is captured, accunting for end terminations and strong curvature gradients compared to the pitch lengths.